Wells Fargo’s Industrial Stock Focus Amidst New Tariffs: Why Wells Fargo Favors Industrial Stocks Despite New Tariffs As S&P
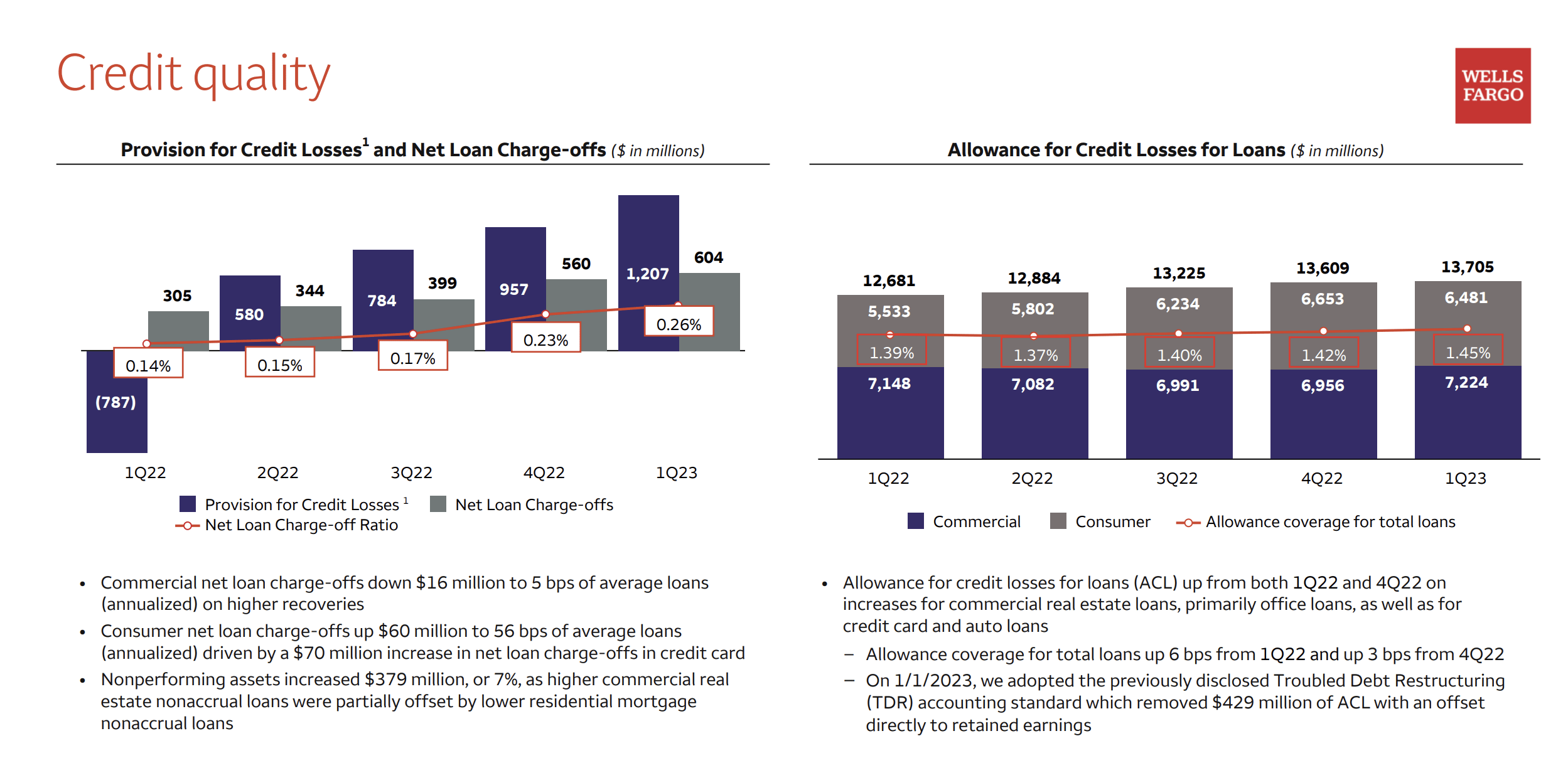
Why Wells Fargo favors industrial stocks despite new tariffs as S&P – Wells Fargo’s investment strategy demonstrates a persistent commitment to the industrial sector, even in the face of challenges posed by newly implemented tariffs. This article delves into the rationale behind this strategy, examining Wells Fargo’s historical investment patterns, risk mitigation techniques, and a comparative analysis against the S&P 500 performance. We will also explore the potential impact of tariffs on industrial stocks and Wells Fargo’s long-term outlook for the sector.
Wells Fargo’s Investment Strategy: Industrial Sector Focus, Why Wells Fargo favors industrial stocks despite new tariffs as S&P

Wells Fargo has historically maintained a significant allocation to industrial stocks, reflecting a belief in the long-term growth potential of this sector. This focus is driven by several factors, including the industrial sector’s role in economic growth, the potential for innovation and technological advancements, and the presence of established companies with strong fundamentals. The bank’s continued focus on industrial stocks, despite current economic uncertainties including tariffs, suggests a long-term perspective and a belief in the resilience of select industrial companies.
While precise comparative data on Wells Fargo’s industrial stock allocation versus other major financial institutions is not publicly available, it is generally understood that many investment firms hold substantial positions in the industrial sector. However, the specific weighting and individual stock selections may vary considerably depending on each institution’s investment philosophy and risk tolerance. Wells Fargo’s specific approach prioritizes companies demonstrating strong financial performance, robust management teams, and a competitive advantage within their respective markets.
Examples of industrial companies favored by Wells Fargo (note: this is not an exhaustive list and actual holdings are subject to change) might include companies like Deere & Company (agricultural machinery), Caterpillar (construction and mining equipment), and Union Pacific (railroad transportation). These companies are selected based on their proven track record, market leadership, and potential for future growth, even in a challenging economic environment.
Impact of New Tariffs on Industrial Stocks
New tariffs can significantly impact industrial companies, potentially reducing profitability and hindering growth. The increased cost of imported raw materials and components directly impacts production costs, while retaliatory tariffs from other countries can limit export opportunities. This can lead to reduced competitiveness, lower profit margins, and potentially job losses.
Sectors particularly vulnerable to tariff-related disruptions include those heavily reliant on imported inputs or those exporting a significant portion of their production. For example, the automotive industry, which relies on globally sourced parts, is highly susceptible to tariff increases. Similarly, manufacturers of steel and aluminum, given the cyclical nature of these industries and the imposition of tariffs on these materials, face heightened sensitivity.
Wells Fargo mitigates tariff-related risks through a combination of strategies, including diversification across various industrial sub-sectors and geographic regions. Thorough due diligence and stress testing of investment portfolios help assess potential vulnerabilities. Moreover, the bank likely incorporates tariff-related risks into its valuation models, adjusting investment decisions accordingly.
| Industrial Sub-Sector | Projected Tariff Impact (Low) | Projected Tariff Impact (Medium) | Projected Tariff Impact (High) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive | -2% to -5% | -5% to -10% | -10% to -15% |
| Steel | -1% to -3% | -3% to -7% | -7% to -12% |
| Chemicals | -2% to -4% | -4% to -8% | -8% to -13% |
| Machinery | -1% to -3% | -3% to -6% | -6% to -10% |
Note: These are hypothetical examples for illustrative purposes only and do not represent actual Wells Fargo projections. Actual impact will vary depending on numerous factors.
Wells Fargo’s Risk Assessment and Mitigation Strategies
Wells Fargo employs sophisticated quantitative and qualitative models to evaluate industrial stock investments. These models incorporate a wide range of factors, including financial performance, industry trends, macroeconomic conditions, and geopolitical risks. The assessment process aims to identify both potential upside and downside risks, enabling informed investment decisions.
Diversification is a cornerstone of Wells Fargo’s risk mitigation strategy. The bank diversifies across various industrial sub-sectors, geographic regions, and company sizes to reduce the impact of any single event or sector-specific downturn. Furthermore, hedging strategies may be employed to mitigate specific risks, such as currency fluctuations or commodity price volatility.
Wells Fargo has a history of navigating economic uncertainty successfully. While specific details of past instances are not publicly available for competitive reasons, the bank’s long-standing presence and experience in the financial markets suggest a robust framework for managing risk and adapting to changing economic conditions. Past successes are likely attributable to the bank’s rigorous risk management practices and ability to identify and capitalize on opportunities.
- Financial strength and stability of the company
- Competitive landscape and market share
- Management team quality and experience
- Technological innovation and adaptability
- Regulatory environment and compliance
- Geopolitical factors and global economic conditions
Comparison to S&P 500 Performance

A direct comparison of Wells Fargo’s industrial stock portfolio performance against the S&P 500 requires access to proprietary data, which is generally not publicly disclosed. However, a general comparison can be made. In periods of strong economic growth, the industrial sector often outperforms the broader market, as reflected in the S&P 500. Conversely, during economic downturns or periods of heightened uncertainty, the industrial sector may underperform.
A hypothetical chart illustrating the relative performance would show two lines: one representing the cumulative return of Wells Fargo’s industrial stock portfolio and the other representing the S&P 500 index over the past five years. The x-axis would represent time (in years), and the y-axis would represent the percentage change in value. The chart would highlight periods of outperformance and underperformance by Wells Fargo’s portfolio relative to the S&P 500. Trends might reveal periods of stronger performance for industrial stocks, potentially correlated with economic expansions, and periods of underperformance during economic contractions or periods of heightened uncertainty. Any discrepancies in performance would be attributable to a variety of factors, including sector-specific dynamics, company-specific performance, and market sentiment.
Wells Fargo’s justification for its industrial stock focus, even if it occasionally underperforms the broader market, rests on its long-term outlook for the sector and its belief in the resilience of selected companies. The bank likely views the potential for long-term growth in specific industrial sub-sectors as outweighing the risks of short-term underperformance relative to the broader market.
Long-Term Outlook for Industrial Stocks
The long-term outlook for industrial stocks is contingent on several factors, including global economic growth, technological advancements, and geopolitical stability. Under various economic scenarios, including sustained growth, moderate growth, and recession, the industrial sector’s performance will vary. However, the long-term growth potential remains significant, particularly in areas such as automation, renewable energy, and infrastructure development.
Wells Fargo’s projections for specific industrial sub-sectors will likely reflect these underlying trends. Sectors with strong growth potential, such as renewable energy and advanced manufacturing, are likely to receive increased attention. Potential growth drivers include government investments in infrastructure, the adoption of automation technologies, and the increasing demand for sustainable products and services. Emerging trends, such as the increasing adoption of artificial intelligence and the Internet of Things (IoT) in industrial processes, will significantly influence investment decisions.
- Global economic growth and stability
- Technological advancements and innovation
- Government policies and regulations
- Infrastructure development and investment
- Commodity prices and supply chain dynamics
- Geopolitical risks and international trade relations


